
Intellectual Property Strategy
Basic Approach and Policy
Intellectual Property Management Strategies to Lead Sustainable Innovation Creation
Intellectual Property Management Philosophy
The Nabtesco Group has positioned its intellectual property as a core value generating competitiveness in the pursuit of sustainable growth and expansion in business for all of its stakeholders, including customers and partner companies. It seeks to bolster corporate value by developing its Intellectual Property Management Strategy, which focuses on protecting and enhancing competitive advantages, across the Group.
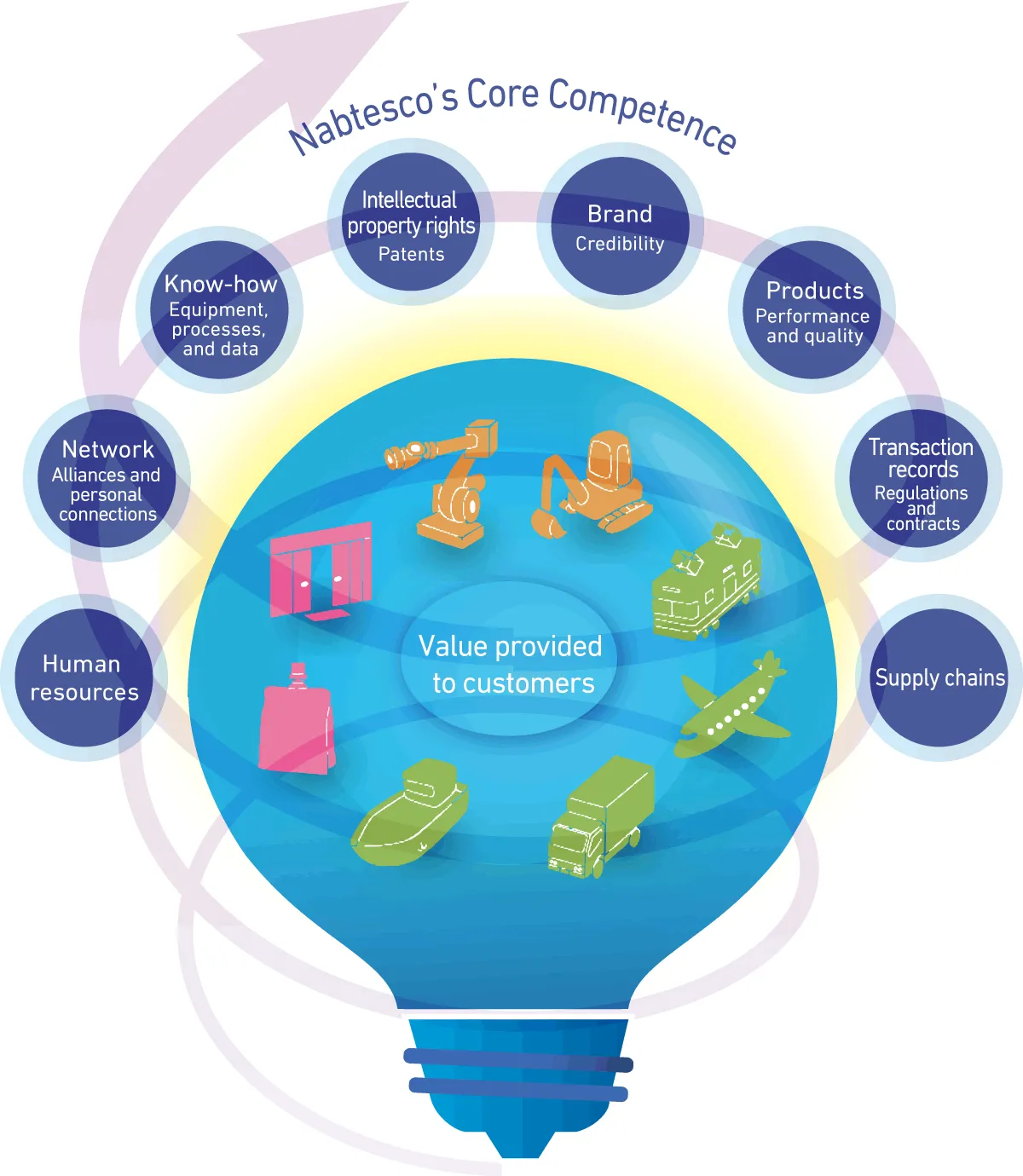
Nabtesco‘s Core Competence
Nabtesco’s Core Competence entails not only so-called core competence (core strengths) but also the technologies, etc. necessary to provide value to customers, even those owned by competitors.
Since we cannot provide value to customers with core competence alone, we refer to a broader scope which includes intellectual properties and intangible assets that cover not only intellectual property rights such as patents, but also know-how, transaction records, and supply chains.
We also determine the core competence we currently hold (current core competence) and the core competence we will need in the future (future core competence) for each business.
In addition, current and future core competences are visualized and shared in a company-wide perspective (functions and objectives).

Adding Intellectual Property Creation to the Criteria for Performance Evaluation
Since FY2017, we have systematized the Intellectual Property Strategy activities to acquire and reinforce our core competence (intellectual properties and intangible assets) by adding Intellectual Property Creation to the criteria for evaluating the performance of in-house companies and Group companies. Each of the in-house and Group companies is now obliged to develop Intellectual Property Strategy activities as business plans for each fiscal year, as set forth in the Medium-Term Business Plan of each in-house company and Group companies, and to implement them accordingly.

The company’s founding anniversary ceremony
Furthermore, the Nabtesco Group strives to develop a corporate culture facilitating the creation of new businesses, ideas about new technologies, and design/manufacturing know-how among all engineers. To this end, employees are encouraged to be proactive as part of an evaluation target for business performance of respective in-house companies. In an attempt to motivate individual employees to become more innovative, Nabtesco gives awards to engineers with spectacular innovations which contribute our business (a total of 182 engineers have been awarded until 2022), to honor their achievements at a ceremony for the corporate foundation anniversary.

A badge given to excellent in-house inventors
As a result of these activities, the number of notifications on intellectual property creation related to inventions, designs and know-how has seen consistent growth, reaching 5 times the FY2013 level in FY2022, as indicated by the following chart:

Inventions that contributed to the company’s businesses displayed at the entrance of the head office
Number of notifications on intellectual property creation
*FY2015 data have been annualized due to changes in the accounting period
Measures to Promote Innovation Through Intellectual Exploration
As part of efforts to stimulate innovation through so-called intellectual exploration, we have been promoting activities to increase diversity of intellectual property creators since 2022. The ratio of inventors has been set as an indicator for such activities.
The ratio of inventors is the ratio of actual number of inventors who notified intellectual property creation to the total number of our engineers including not only those engaging in development but also production engineers. The ratio, which is calculated in each financial year, indicates whether diversity is maintained and improved on a continuous basis.
In addition, we will strive to promote innovation as a unified team across the company based on the system for intellectual property creation supporters, such as sales representatives who have identified new market needs and brought about innovation.
Ratio of inventors (including know-how and design inventors)
Protecting the future of business and the products of customers
With these initiatives, Nabtesco has sought to accelerate and diversity the innovative creation by enhancing individual employees’ creativity while balancing intellectual exploration and exploitation to further increase its core competence (intellectual properties and intangible assets).
For the Nabtesco Group, having expanded its businesses based on the trust of industry-leading customers in many fields, the Intellectual Property Management Strategy also is a strategy to raise the Group’s corporate value by protecting the business and products of its customers, now and in the future. In order to realize sustainable and profitable growth with all stakeholders, including customers and partner companies, the Nabtesco Group’s intellectual property activities will continue to evolve.
System
System to Implement Intellectual Property Strategies
Nabtesco has a system to implement its intellectual property strategies. The main components of the system are the following three organizations.
The first is the Group Intellectual Property Strategy Committee comprising Nabtesco’s CEO, corporate officers, the presidents of its in-house companies, the presidents of Group companies, and other members of the management team. They meet to deliberate on the basic policies for the group-wide intellectual property strategies.
The second organization is the Nabtesco Intellectual Property Strategy Subcommittee composed of the general manager of the administrative departments and general managers and those in similar positions in charge of enhancing the intellectual property-related abilities of the in-house companies and Group companies (hereinafter collectively “in-house companies, etc.”), who are appointed by the presidents, etc. of the in-house companies, etc. At this Committee’s meetings, based on the understanding of the basic policies decided by the Group Intellectual Property Strategy Committee, participants share information about the activities related to intellectual property strategies conducted by individual in-house companies, etc. and deliberate on the group-wide intellectual property enhancement measures for common issues faced by individual in-house companies, etc. to generate synergy effects across the board.
The third organization is the Company Intellectual Property Strategy Committee. It is established by each of the in-house companies, etc. and composed of the presidents of the in-house companies, etc. and the general managers in charge of the departments of the in-house companies, etc. In reference to the basic policies set by the Group Intellectual Property Strategy Committee and to the information about the in-house companies’ intellectual property strategy-related activities shared at the meetings of the Nabtesco Intellectual Property Strategy Subcommittee, members of this organization deliberate on the intellectual property strategies specific to the in-house companies, etc. such as the strategies for the creation of intellectual property, utilization of the intellectual property rights, and development of new markets and new products.
Based on the organic collaboration of the aforementioned three organizations, the Nabtesco Group has thus established an optimal system to implement its intellectual property strategies.
In addition, the Board of Directors supervises the activities related to intellectual property strategies by these three executive organizations.
Implementation and Oversight Structure for Implement Intellectual Property Strategies

Measures
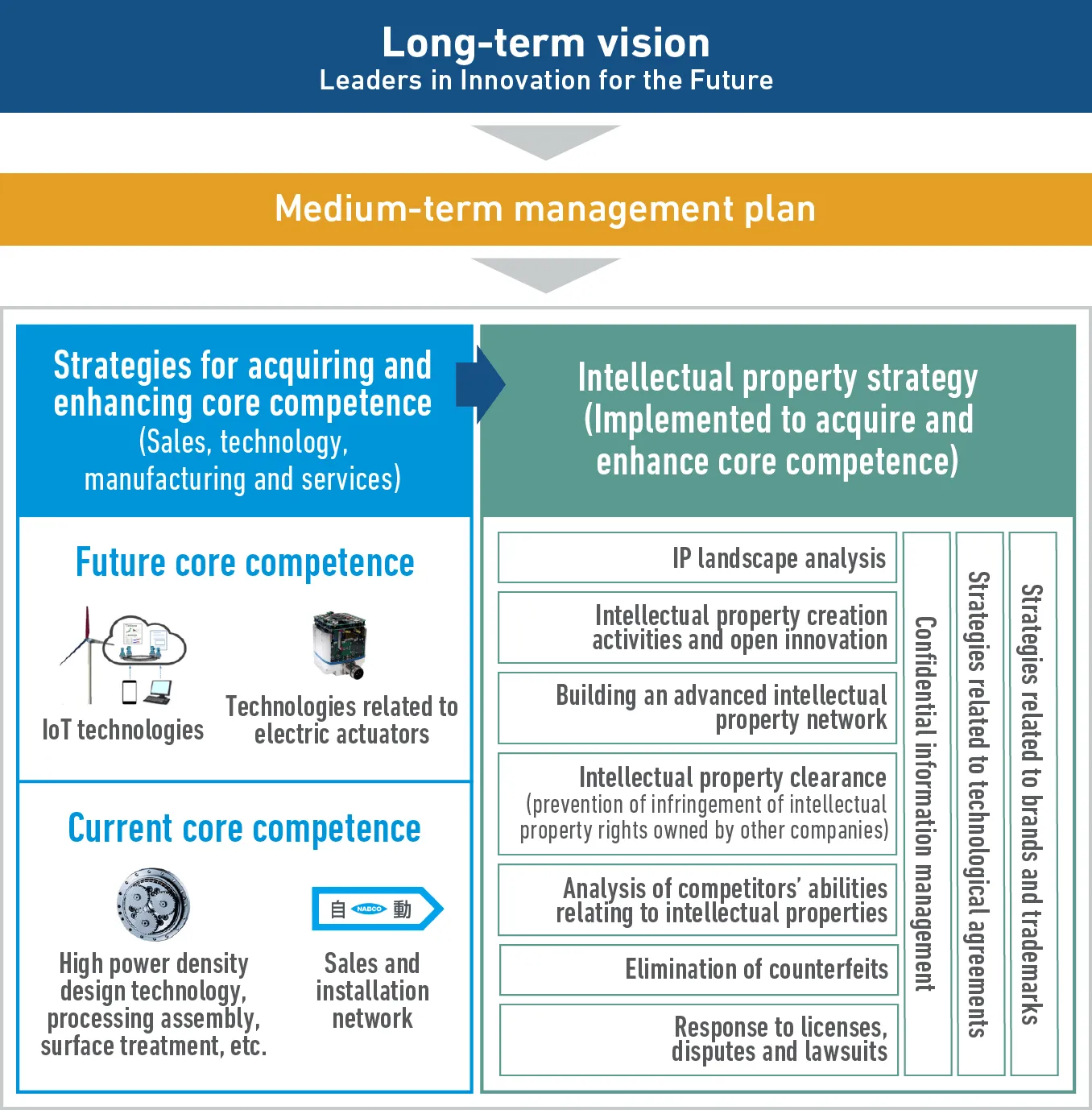
Overall Picture of Intellectual Property Strategy —Acquisition and Enhancement of Core Competence—
Relationship Between Strategies for Acquiring and Enhancing Core Competence and Intellectual Property Strategy
Based on the long-term vision, each in-house company formulates a medium-term management plan. Based on this plan, strategies for acquiring and enhancing core competence are formulated by each in-house company in order to acquire the current core competence (such as high power density design technology, processing assembly and surface treatment, sales and installation network) and the future core competence (such as IoT technologies and technologies related to electric actuators).
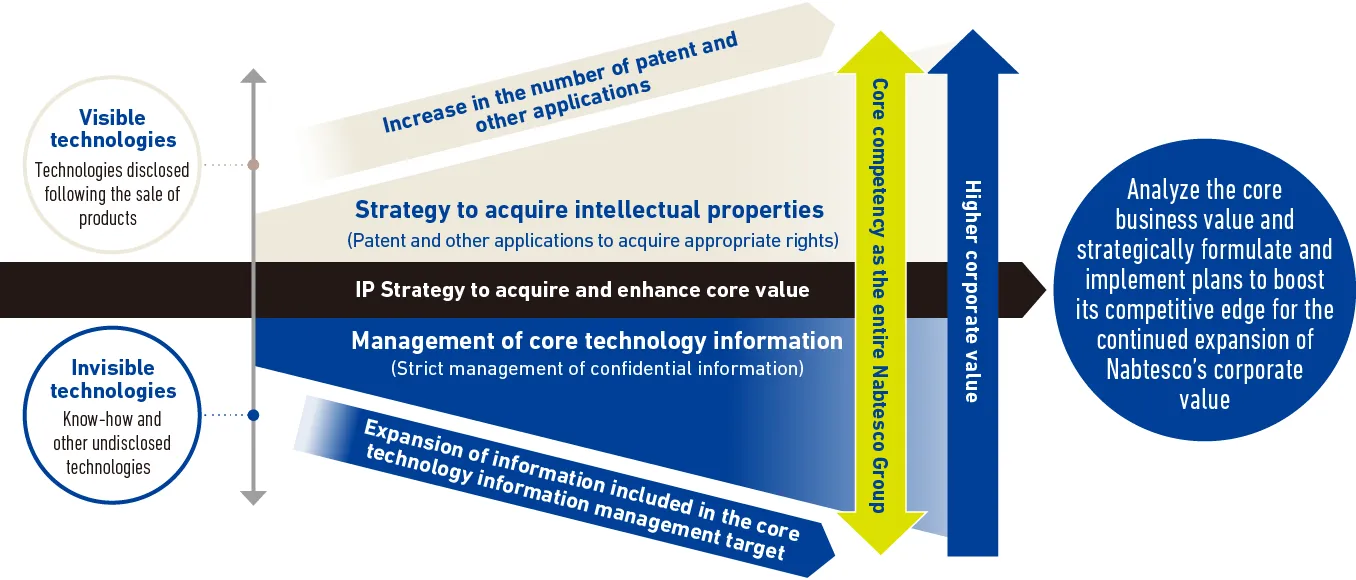
The intellectual property strategy of the Nabtesco Group is to acquire and enhance core competence (intellectual properties and intangible assets) by implementing strategies related to intellectual properties through the following activities: IP landscape analysis using intellectual property information to identify technological trends; intellectual property creation activities including open innovation using the results of IP landscape analysis; building an advanced intellectual property network to acquire intellectual property rights from the early stage of development; intellectual property clearance to prevent Nabtesco Group’s products and services from infringing on intellectual property rights owned by other companies; analysis of competitors’ abilities relating to intellectual properties; elimination of counterfeits; licenses, disputes and lawsuits; confidential information management to strictly protect the know-how (core technological information) of the Nabtesco Group; strategies related to technological agreements; and strategies related to brands and trademarks for protecting and utilizing Nabtesco’s corporate brand.
Relationship Between Strategies for Acquiring and Enhancing Core Competence and Intellectual Property Strategy
IP Intelligence: Formulation of Measures to Increase Competitiveness
The Nabtesco Group capitalizes on its IP intelligence when formulating the measures for acquiring and enhancing core competence. Specifically, the current core competence (intellectual properties and intangible assets) of the in-house companies and Group companies are compared and analyzed in terms of the level of response to customer needs and competitiveness against peer companies from the perspectives of businesses and intellectual properties. Based on the results of this analysis, we have identified the gap between the current core competence and the future core competence, and have formulated measures for acquiring and enhancing core competence to maintain and improve our business competitiveness.
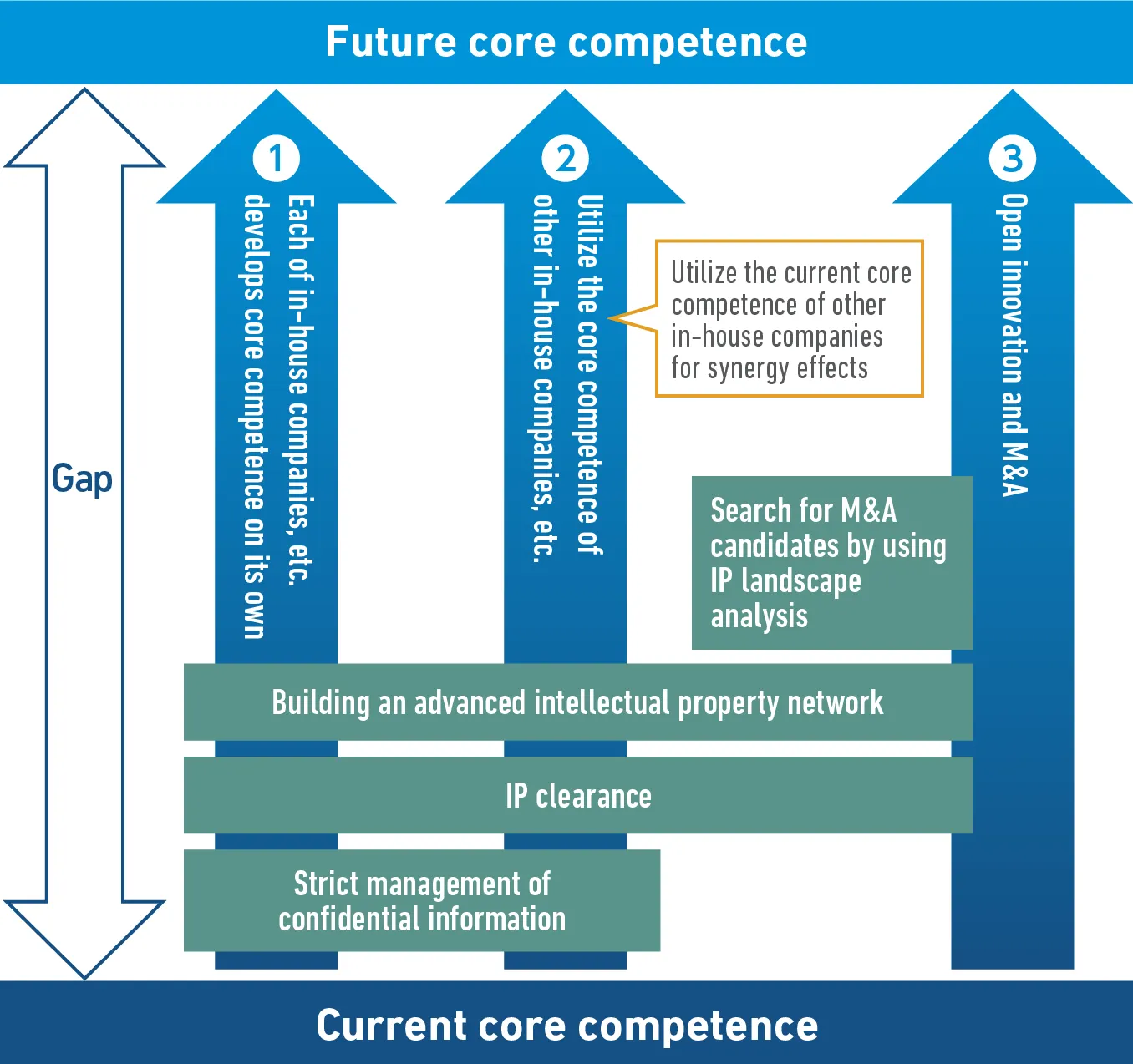
Activities Related to Intellectual Property Strategies Aimed at Acquiring the Future Core Competence
There are three main ways to bridge the gap between the current core competence and the future core competence. The first is that each business develops core competence on its own. The second is to utilize the core competence (intellectual properties and intangible assets) of other in-house companies and Group companies. The third is to utilize open innovation and M&A.
When developing core competence on its own or utilizing the core competence (intellectual properties and intangible assets) of other in-house companies, etc., building an intellectual property network, intellectual property clearance, and confidential information management are the focus of the activities related to intellectual property strategies.
As for open innovation and M&A, searching for and evaluating M&A candidates by using IP landscape analysis, building an intellectual property network, and IP clearance are the focus of the activities related to intellectual property strategies.
As the Nabtesco Group has been conducting business in various fields for many years, the level of core competence (intellectual properties and intangible assets) held by individual in-house companies, etc. is high and diverse. Therefore, by building on the current core competence (intellectual properties and intangible assets) of other in-house companies, etc., it will be possible to acquire the future core competence (intellectual properties and intangible assets) of other in-house companies, etc. more quickly.
Activities Related to Intellectual Property Strategies Aimed at Acquiring the Future Core Competence
Examples of the current core competence held by in-house companies, etc. (Only patents and utility models are shown in the landscape map)
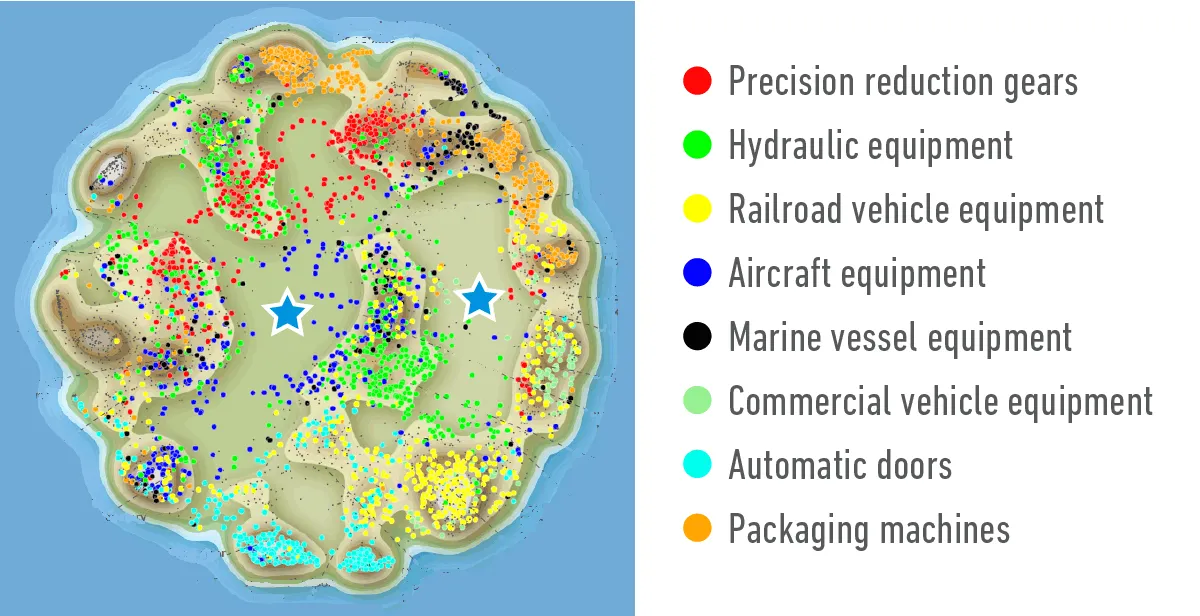
*Prepared based on the parent and utility model applications by the Nabtesco Group in Japan and overseas announced as of the end of October 2021
- The dots represent patent applications and similar parent applications are located close to each other.
- Mountains and valleys are represented as a topographic map according to the density (number) of dots.
Strategies for Acquiring and Enhancing Core Competence in Accordance with Market Characteristics
The Nabtesco Group has been promoting activities for acquiring and enhancing core competence (intellectual properties and intangible assets), taking into account market characteristics while utilizing the theory of economics and management.
Creation of New Businesses through IP Landscape, New Frontier Markets and Customer Needs to Explore
Objectives for Conducting IP Landscape Analysis
IP landscape differs from so-called patent maps in that it includes information on trends in research and development, management strategies, etc. of our company, our competitors and markets as well as technological information such as individual patent. It provides an overview of our current market position and future prospects.
As the analysis is conducted based on information available on the public domain, corporate information we can see on IP landscape is limited. However, intellectual property information available on IP landscape, such as patent applications, includes not only the technologies currently used but also the technologies that may be used in the future as well as issues to be resolved. Therefore, we will be able to enhance the accuracy of our business strategy by using IP landscape analysis.

Classification and Case Study of IP Landscape Activities
The following table represents IP landscape activities in the form of Ansoff’s growth matrix. For example, when we provide new products and services to the existing markets, we conduct an analysis of customer needs to grasp technological trends and issues faced by customers.
We use the analysis results to set our future business policies and hold discussions with in-house companies, etc. about collaborations with other companies, by searching for new business themes, market and customer needs, examining development themes, and finding new business partners to foster open innovation.
We have conducted these activities by selecting more than 60 group-wide themes and more than 100 themes specific to in-house companies and Group companies since 2017.
Classification of IP Landscape Activities

IP Landscape Case Study: Identifying Market Needs
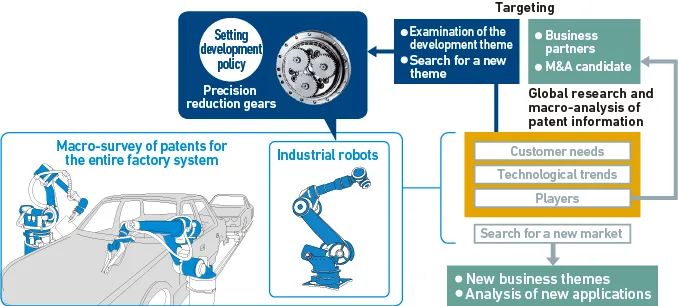
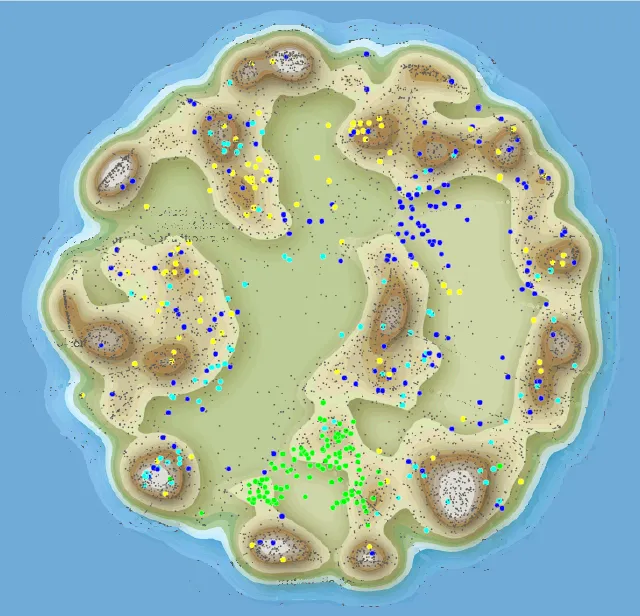
IP Landscape Case Study: Analysis of the Nabtesco Group’s Core Competence

*Prepared based on the parent and utility model applications by the Nabtesco Group in Japan and overseas announced as of the end of October 2021
- The dots represent patent applications and similar parent applications are located close to each other.
- Mountains and valleys are represented as a topographic map according to the density (number) of dots.
- Overlapped areas: Fields in which core competence can be expanded horizontally by leveraging common technologies
- Areas represented with valleys (stars): Fields subject to the enhancement of core competence and the consideration of combination
IP Landscape Case Study: Analysis of the Nabtesco Group’s Core Competence Related to SDGs
Category of relevant patents, etc.
●
- Related to wind power generation equipment
- Related to improvement of energy use efficiency and reduction of loss
●
- Related to platform doors
- Related to safe operation of buses
●
- Related to the reduction in size and weight (mobility related/other than construction machinery)
- Related to life extension/durability improvement/disposal/recycling
●
- Related to the reduction in weight (mobility related, construction machinery)
- Related to efficiency improvement, compliance with emission regulations in various countries, and electrification of actuators
*Prepared based on the parent and utility model applications by the Nabtesco Group in Japan and overseas announced as of the end of October 2021
- The dots represent patent applications and similar parent applications are located close to each other.
- Mountains and valleys are represented as a topographic map according to the density (number) of dots.
- Nabtesco’s products and services indirectly support the response to SDGs in customer’s businesses
- Continue to focus on the creation of intellectual properties related to SDGs
IP Landscape Case Study: Co-Creation, Searching for M&A Candidates, Complementary Relationship
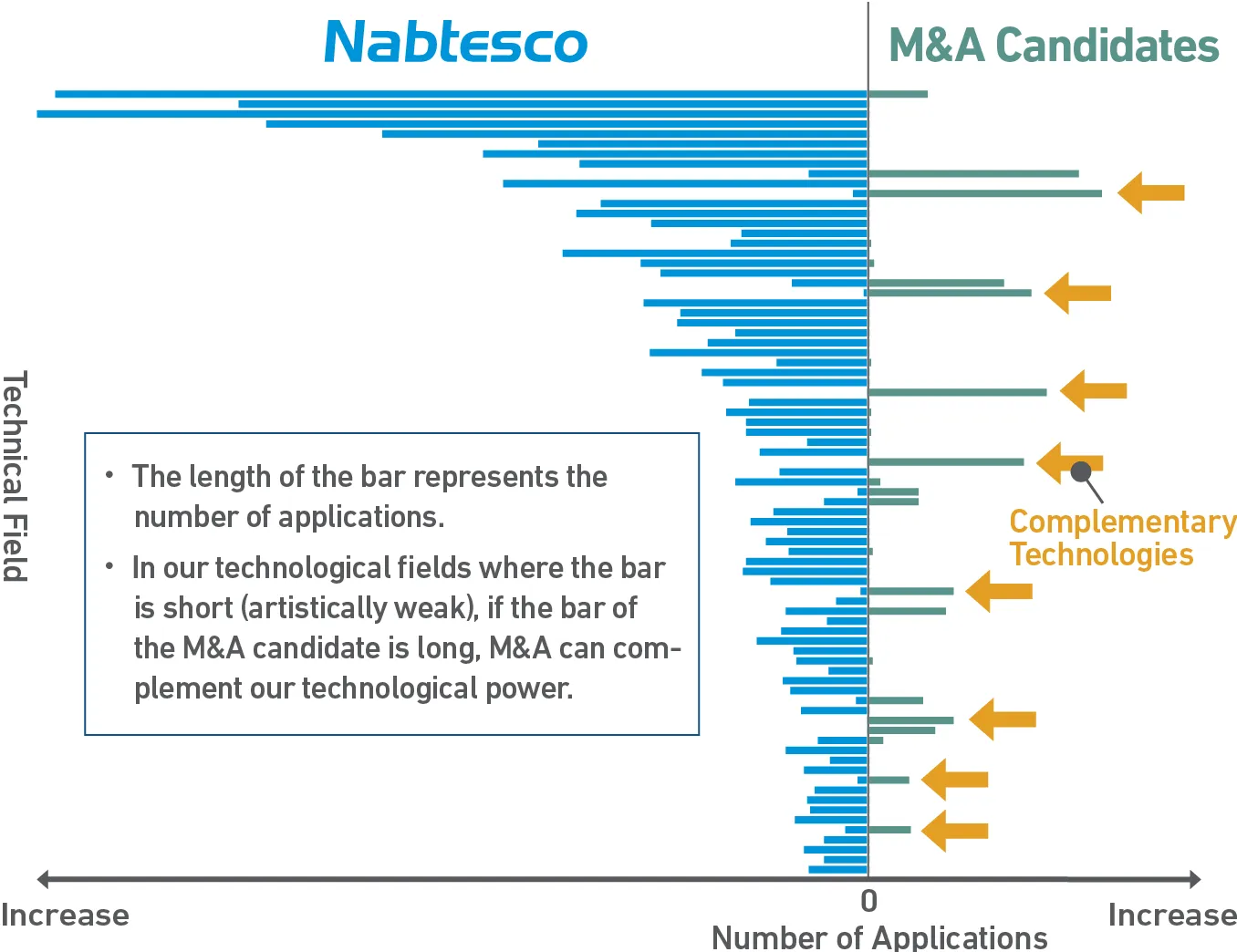
By comparing the patent application status of Nabtesco and M&A candidates by technology field, it is possible to grasp the existence of complementary relationship from the technological perspective.
Survey on patent applications related to offshore wind turbine system on the whole
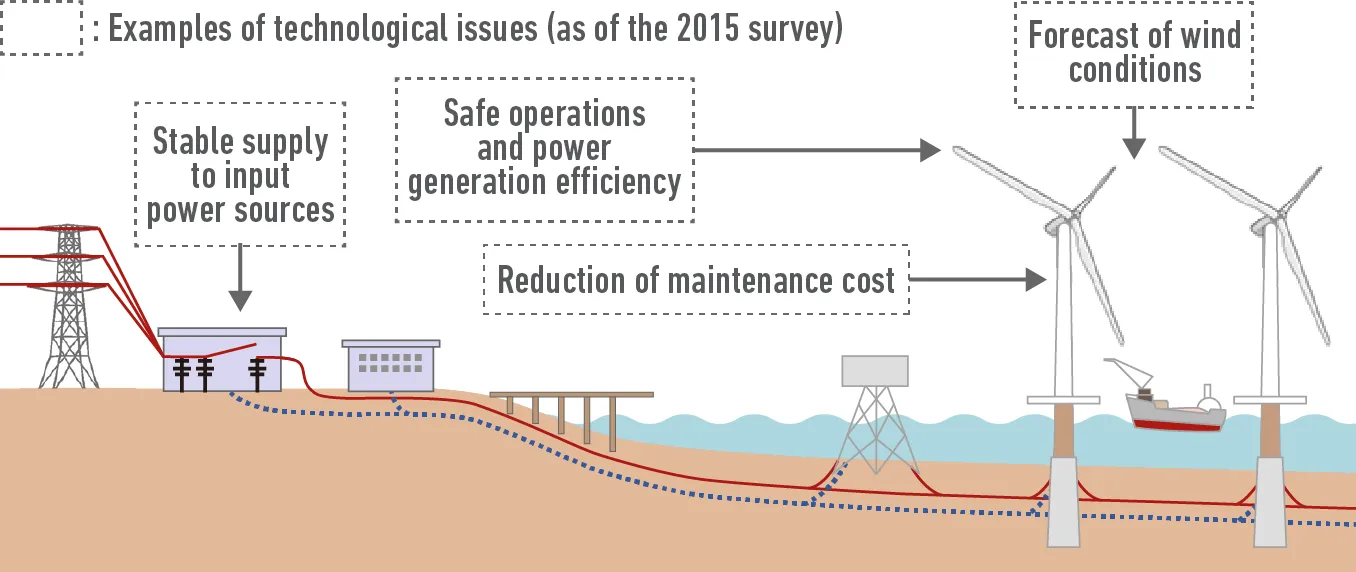
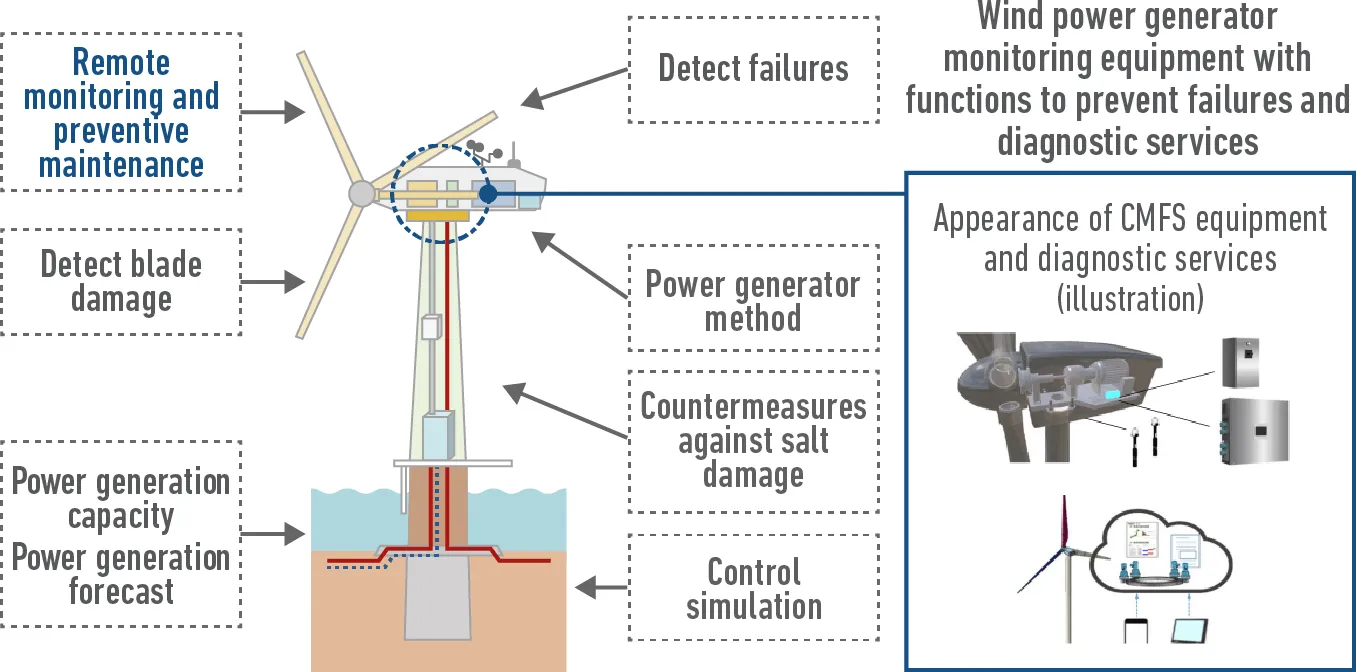
*Source: The above diagram was prepared by citing a diagram included in NEDO’s White Paper on Renewable Energy: Chapter III Wind Power Generation.
Grasp true customer needs by analyzing the entire system
→Utilize them for the development of individual products and services
Confidential Information Management and Strategy to Acquire Intellectual Property Rights
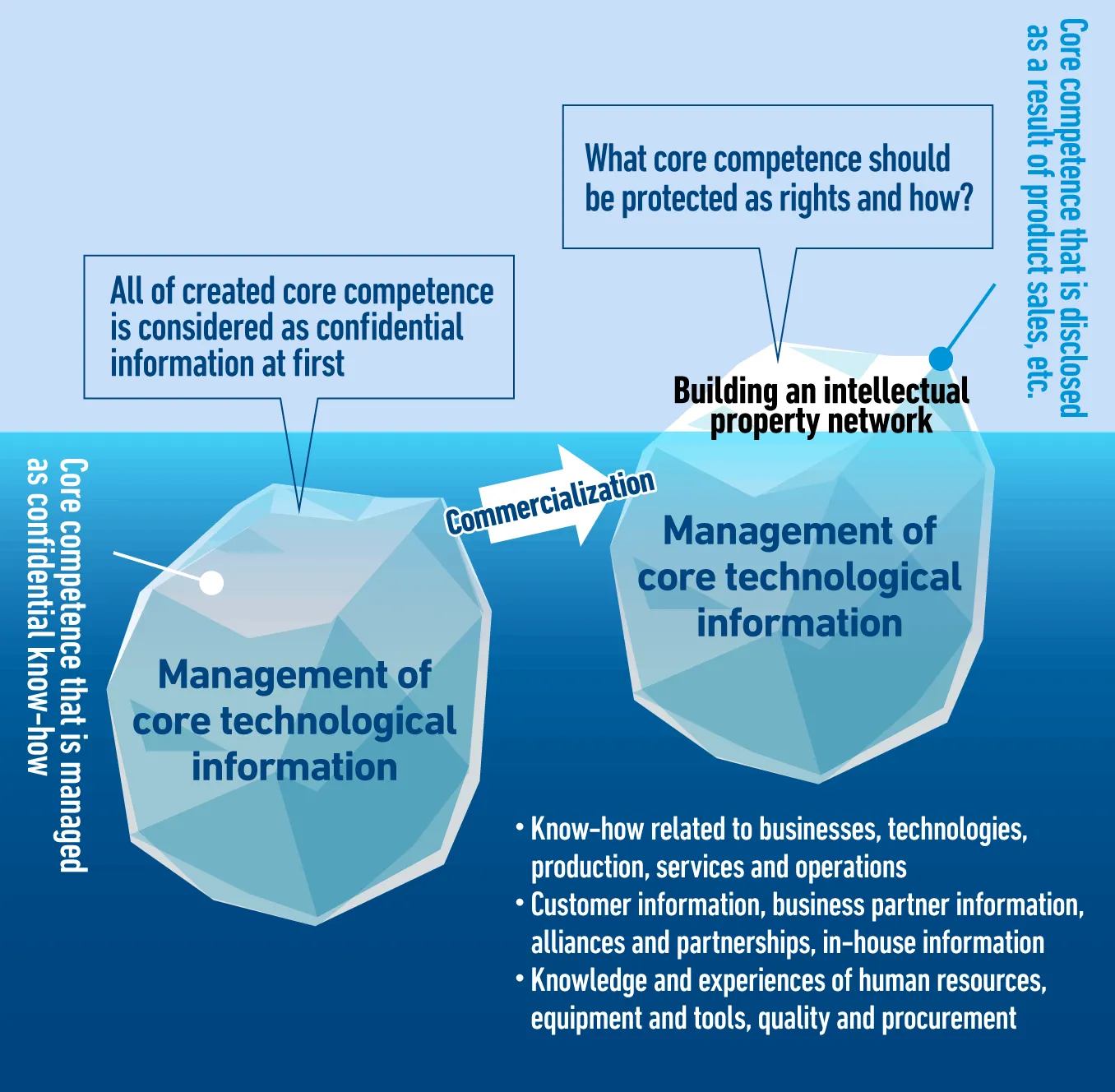
The Nabtesco Group identifies its core value as a source of competitiveness. The Group’s core value includes the unwavering trust of customers, brand perception established in the marketplace and technological as well as design/manufacturing ideas and know-how related to products and services provided. These core value elements, including a number of patents, designs, trademarks and marketing intelligence, are protected by safeguards for intellectual assets.
As for created core competence (intellectual properties and intangible assets), we impose strict management controls to protect it as core technological information (confidential information) in principle. As part of our efforts to manage core technological information, we provide information management education to all officers and employees (including temporary staff) every year and ensure to collect evidences that can be valid in trials in Japan and overseas. In addition, we endeavor to maintain the management system in collaboration with the Business Auditing Department.
Meanwhile, for technological core competence that cannot be kept confidential because we disclose it in our business activities such as product sales, we protect it based on our strategy to acquire intellectual property rights by building an intellectual property network. As of the end of 2022, we have built the intellectual property network comprising a number of patents, utility models, and designs (including those under application) (more than 2,300 cases in Japan, more than 1,700 cases in Asia, more than 1,100 cases in Europe, and more than 500 cases in the Americas).
We will protect our current core competence as well as our future core competence which is yet to be created through the management of core technological information and the strategy to acquire intellectual property rights, thereby continuing to enhance the Nabtesco group’s comprehensive ability regarding intellectual properties and intangible assets and increase our corporate value.
Basic concept of protecting technological core competence
Intellectual Property Strategy to Acquire and Enhance Core Value
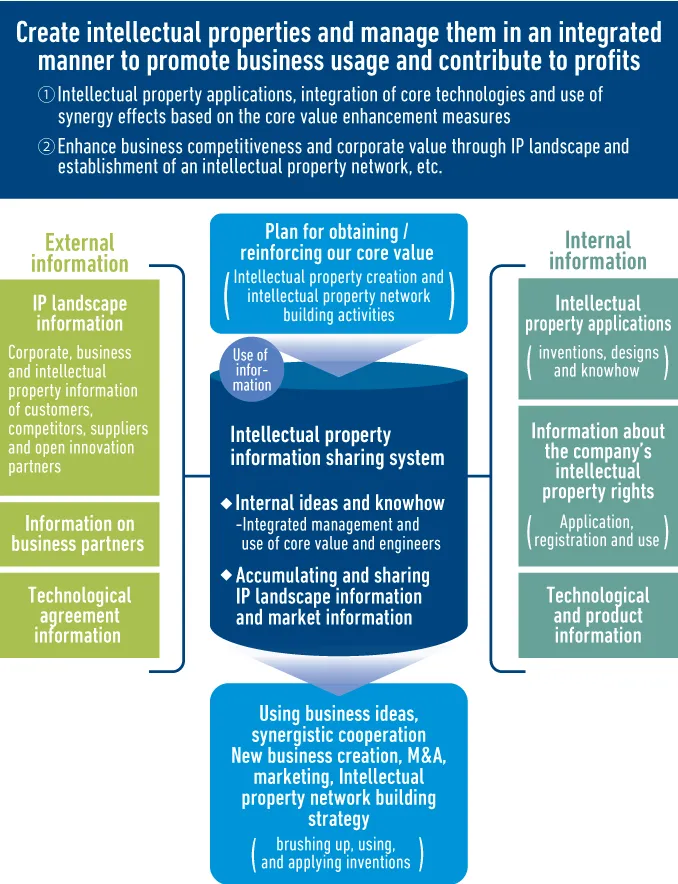
Database of Intellectual Property Information Sharing System
For creating intellectual property and acquiring intelligence property rights based on the plan for acquiring and enhancing our core competence, we have introduced a one-stop intellectual property information sharing system that can search for and refer to intellectual property notifications regarding ideas, know-how, designs, etc. created internally as core competence (intellectual properties and intangible assets) as well as IP landscape analysis results and technical agreements, thereby promoting internal information sharing and the utilization of intellectual properties for new business creation, M&A, building of an intellectual property network, and other business operations.
Future Outlook: Integrated Management of Intellectual Properties and Promotion for Business Usage
Execution of Intellectual Property Clearance
Since Nabtesco Group considers protecting customer’s business and products as an essential factor, Group conducts intellectual property clearance as a part of the commercialization process, making it essential to protect customers’ businesses and products. More specifically, it undertakes activities during the commercialization process, including those related to core technology information management, the acquisition of intellectual property rights, protection against the infringement of intellectual property right by other companies, compliance with technological agreements, anti-counterfeiting, and the protection of trademarks or copyrights.
We have conducted intellectual property clearance for more than 80 products and services since 2018.
Intellectual Property Risk Management: The Execution of Intellectual Property Clearance

Elimination of Counterfeits
In order to ensure that customers who trust Nabtesco’s brand and purchase its products do not suffer any damage, the Nabtesco Group has a policy of thoroughly eliminating counterfeits of its brands, even if it incurs costs.
In addition to information from in-house companies and Group companies within and outside Japan, we visit exhibitions and monitor the status of listings on EC sites and corporate websites on a regular basis, and periodically monitor companies that stopped infringing on our products after warning them in the past in an effort to detect any counterfeits as soon as possible.
As a result, we have provided more than 240 infringement warnings since 2019.



